Latest Post
Optimization: Exhaustive Search Method
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Exhaustive Search Method Opimization Algorithm in C
#include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>
double myFun(double x);
int main()
{
double a, b, N, y, x, x1, x2, x3, fx1, fx2, fx3, D,i=0;
printf("Enter a:");
scanf("%lf",&a);
printf("Enter b:");
scanf("%lf",&b);
printf("Enter no. of N:");
scanf("%lf",&N);
D = (b-a)/N;
printf("D = %.2lf",D);
x1=a;
x2=x1+D;
x3=x2+D;
jump:
if (i < 300)
{
printf("\n\nx1 = %.2lf",x1);
printf("\nx2 = %.2lf",x2);
printf("\nx3 = %.2lf",x3);
fx1 = myFun(x1);
printf("\nf(x1) = %.2lf",fx1);
fx2 = myFun(x2);
printf("\nf(x2) = %.2lf",fx2);
fx3 = myFun(x3);
printf("\nf(x3) = %.2lf",fx3);
if (fx1 >= fx2 && fx2<= fx3)
{
printf("\nCondition met");
goto end;
}
else
{
printf("\nCondition not met.");
x1 = x2;
x2 = x1 + D;
x3 = x2 + D;
i = i + 1;
goto jump;
}
}
else
{
goto end;
}
end:
return 0;
}
double myFun(double x) // function definition
{
double y;
y = ((x*x)+(54/x));
return y; // return statement
}
Output:
 |
| Exhaustive Search Algorithm |
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular posts from this blog
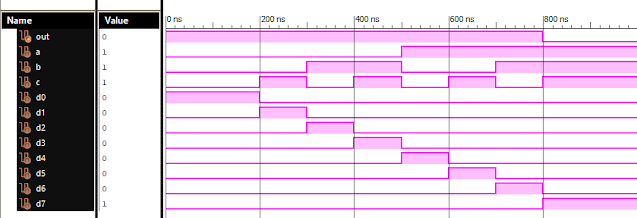
Verilog: 8 to 1 Multiplexer (8-1 MUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
Verilog Code for 8 to 1 Multiplexer Dataflow Modelling module mux_8to1( input a, input b, input c, input D0, input D1, input D2, input D3, input D4, input D5, input D6, input D7, output out, ); module m81( output out, input D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, S0, S1, S2); assign S1bar=~S1; assign S0bar=~S0; assign S2bar=~S2; assign out = (D0 & S2bar & S1bar & S0bar) | (D1 & S2bar & S1bar & S0) | (D2 & S2bar & S1 & S0bar) + (D3 & S2bar & S1 & S0) + (D4 & S2 & S1bar & S0bar) + (D5 & S2 & S1bar & S0) + (D6 & S2 & S1 & S0bar) + (D7 & S2 & S1 & S0); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a= 0;b = 0;c = 0;D0 = 1;D1 = 0;D2 = 0;D3 = 0;D4 = 0;D5 = 0;D6 = 0;D7 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a = 0;b = 0;c = 1;d0 = ...
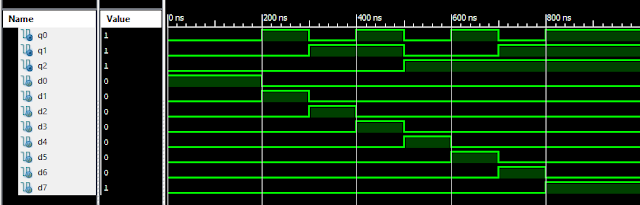
VLSI: 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling module encoder_8_to_3( input d0, input d1, input d2, input d3, input d4, input d5, input d6, input d7, output q0, output q1, output q2 ); assign q0 = ( d1 | d3 | d5 | d7 ); assign q1 = ( d2 | d3 | d6 | d7 ); assign q2 = ( d4 | d6 | d5 | d7 ); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling initial begin ...
VLSI: 1-4 DEMUX (Demultiplexer) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_4( input d, input s0, input s1, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3 ); assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s0n = ~ s0; assign y0 = d& s0n & s1n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs ...
Verilog: 2 - 4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling 2-4 Line Decoder module decoder_2_to_4( input a0, input a1, output d0, output d1, output d2, output d3 ); not (an0,a0),(an1,a1); and (d0,an0,an1),(d1,a0,an1),(d2,an0,a1),(d3,a0,a1); endmodule //Testbench code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a0 = 0;a1 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a0=1;a1=0; #100; a0=0;a1=1; #100; a0=1;a1=1; end Output: Verilog 2-4 Decoder Response Other Verilog Programs: Go to Index of Verilog Prog...
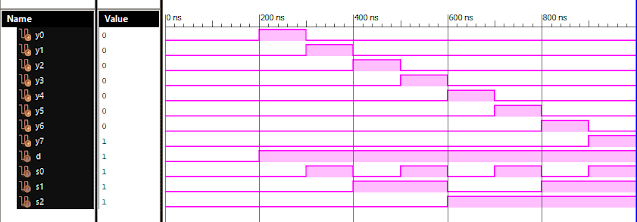
Verilog: 1to 8 DeMultiplexer (1-8 DEMUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
Verilog Code for 1 to 8 DeMultiplexer Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_8( input d, input s0, input s1, input s2, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3, output y4, output y5, output y6, output y7 ); assign s0n = ~ s0; assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s2n = ~ s2; assign y0 = d & s0n & s1n & s2n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n & s2n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1 & s2n; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1 & s2n; assign y4 = d & s0n & s1n & s2; assign y5 = d & s0 & s1n & s2; assign y6 = d & s0n & s1 & s2; assign y7 = d & s0 & s1 & s2; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-8 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs d = 0;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 1; ...


Comments
Post a Comment