Latest Post
Alien Stones from Space !!
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
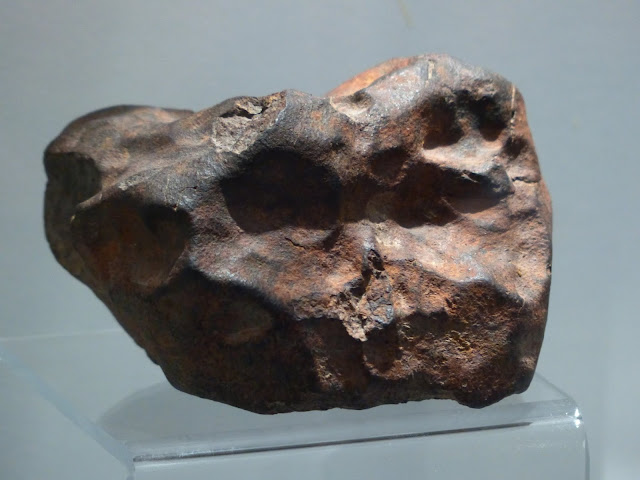
Many people have some unique interesting hobbies, one of that is collection of heavenly stones (Meteorite Stones). We can also find a museum at Chicago called "Garden of Heaven". Garden of Heaven is museum of meteor stones collected from different places and different continents. For some this is business, to hunt for meteor stones and sell at very high price.
Most of the meteors belong to Asteroid belt between orbits of Mars and Jupiter, but few of them belonged to Moon and Mars!! Sometimes when a massive Asteroid hits surface of Mars, small surface objects on mars bounces and leaves gravity of Mars. When such objects are captured by Earth's gravity, they enter into Earth's atmosphere. Similarly different objects arrive from Moon. This is possible because Mars has weak gravity and moon being closest to Earth with very weak gravity.
Mechanic Farmer is a well known name of Meteorite hunter.
Few heavenly rocks found are:
1. E-Mevak found in 1922 in Chile (Opening particles).
2. Aahumda found in Mexico in 1909, kept in Garden of Heaven museum, Chicago.
Axtel found in Texas in 1943, it is Carbonesius Contract.
Martian rock named Sapt Al Uhaymir 008 found in 1999 from Oman.
5. Another Martian Meteorite rock Indark found from Azerbaijan in 1958.
6. Park forest found in Illinois in USA in 2003.
7. Homstick found in 1857.
8. Crab Orchid found in 1887, Tennesse, USA.
Many meteorite rocks found in Antarctica can be easily recognized as meteor rocks because these are found above the snowbed. Antarctica and Arctic region are hot favourite destinations for meteor rock hunting.
These rocks are rated in market depending upon how old is the rock, what the rock is made up of, weight, origin of rock (moon,mars or any Asteroid),etc.
There are passionate buyers who buy these rocks as a hobby or for their museum collection.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular posts from this blog
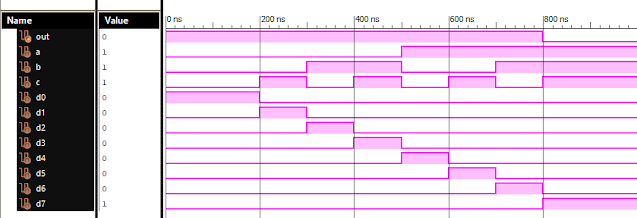
Verilog: 8 to 1 Multiplexer (8-1 MUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
Verilog Code for 8 to 1 Multiplexer Dataflow Modelling module mux_8to1( input a, input b, input c, input D0, input D1, input D2, input D3, input D4, input D5, input D6, input D7, output out, ); module m81( output out, input D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, S0, S1, S2); assign S1bar=~S1; assign S0bar=~S0; assign S2bar=~S2; assign out = (D0 & S2bar & S1bar & S0bar) | (D1 & S2bar & S1bar & S0) | (D2 & S2bar & S1 & S0bar) + (D3 & S2bar & S1 & S0) + (D4 & S2 & S1bar & S0bar) + (D5 & S2 & S1bar & S0) + (D6 & S2 & S1 & S0bar) + (D7 & S2 & S1 & S0); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a= 0;b = 0;c = 0;D0 = 1;D1 = 0;D2 = 0;D3 = 0;D4 = 0;D5 = 0;D6 = 0;D7 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a = 0;b = 0;c = 1;d0 = ...
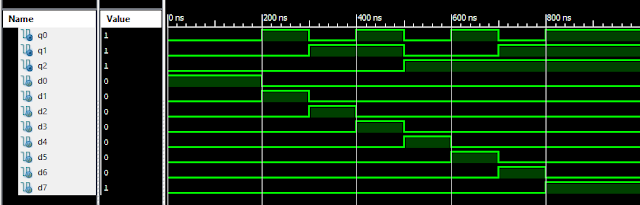
VLSI: 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling module encoder_8_to_3( input d0, input d1, input d2, input d3, input d4, input d5, input d6, input d7, output q0, output q1, output q2 ); assign q0 = ( d1 | d3 | d5 | d7 ); assign q1 = ( d2 | d3 | d6 | d7 ); assign q2 = ( d4 | d6 | d5 | d7 ); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling initial begin ...
VLSI: 1-4 DEMUX (Demultiplexer) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_4( input d, input s0, input s1, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3 ); assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s0n = ~ s0; assign y0 = d& s0n & s1n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs ...
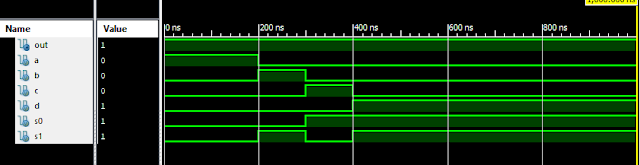
VLSI: 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling module m41(out, i0, i1, i2, i3, s0, s1); output out; input i0, i1, i2, i3, s0, s1; assign y0 = (i0 & (~s0) & (~s1)); assign y1 = (i1 & (~s0) & s1); assign y2 = (i2 & s0 & (~s1)); assign y3 = (i3 & s0 & s1); assign out = (y0 | y1 | y2 | y3); endmodule //Testbench code for 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a = 1;b = 0;c = 0;d = 0;s0 = 0;s1 = 0; ...
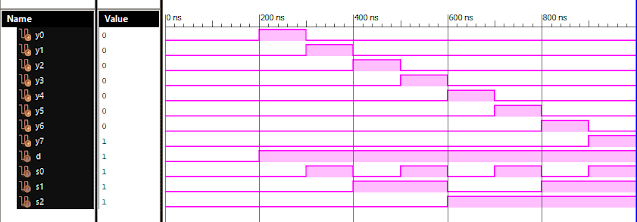
Verilog: 1to 8 DeMultiplexer (1-8 DEMUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
Verilog Code for 1 to 8 DeMultiplexer Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_8( input d, input s0, input s1, input s2, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3, output y4, output y5, output y6, output y7 ); assign s0n = ~ s0; assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s2n = ~ s2; assign y0 = d & s0n & s1n & s2n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n & s2n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1 & s2n; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1 & s2n; assign y4 = d & s0n & s1n & s2; assign y5 = d & s0 & s1n & s2; assign y6 = d & s0n & s1 & s2; assign y7 = d & s0 & s1 & s2; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-8 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs d = 0;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 1; ...


Comments
Post a Comment