Latest Post
Space Facts: Part 3 - Cheapest Interplanatery Mission, Comets, Magnetic Field, Different types of Stars
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Cheapest Interplanetary Spacecraft: Mangalyaan
Mangalyaan mission cost was 450 Crore Rupees.Rocket: PSLV-C25
Organization: ISRO
Mangalyaan spacecraft 150 Crore.
Rocket Cost: PSLV-C25: 110 Crore.
Weight of Mangalyaan: 1350 Kg, out of 1350 Kg, 500 Kg is weignt of spacecraft and rest is fuel weight.
Mangalyaan is also called Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), Travelled for 25 days around earth changing 6 orbits, and 326 days between Earth and Mars.
Comets:
Kuiper Belt and Cloud of Urt are home to most of the comets of our solar-sysem. Some well known comets are:
1. Comet Siding Spring: Took a fly-by near Mars on October 19, 2014.
2. Great Comet of 1980 was the first Comet Registered.
3. Haley's Comet: Passes near Earth every 75 years.
4. Comet Shoemaker Levy 9, a comet that ended up clashing with giant Jupiter! It's the first collision ever recorded by any celestial body in our solar system. When this comet was passing nearby Jupiter due to high gravity of planet, the comet got broken into pieces. Few of it fell on Jupiter and others were spread around elsewhere in space.
5. Harley 2, Comet Ison, Comet Hale-Bopp, Comet 49 Virtaman, Comet Lovjoy (Green Comet)
Magnetic Field of Mars:
Gravitational force of Mars is 38% than that of earth, even Mars has lost it's magnetic field to some extent due to any unknown reason. Jupiter's magnetic field changes with rotation.
Different Types of Stars in Universe:
Pulsar: Crab Nebula is well-known Pulsar star.
Iota Orionis: Type O
Color: Blue
Surface Temperature: 55000 C
Rigel: Type B
Color: Blue-White
Surface Temperature: 36000 C
Sirius, Vega: Type A
Color: White
Surface Temperature: 20000 C
Canopus: Type F
Color: Yellow-White
Surface Temperature: 13500 C
Sun: Type G
Color: Yellow
Surface Temperature: 11000
Arcturus: Type K
Color: Orange
Surface Temperature: 7500 C
Betelgeuse: Type M
Color: Red
Surface Temperature: 5500 C
Pistol Star is Brightest star of our Galaxy, it is blue in color. Antares is a star nearby it.
Arcturus
Betelgeuse
Canopus
Comet Ison
Comet Shoemaker Levy
Comets
Crab Nebula
Haley's Comet.
Mangalyaan
Pistol Star
Rigel
Sirius
Space
Star
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular posts from this blog
Verilog: 8 to 1 Multiplexer (8-1 MUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
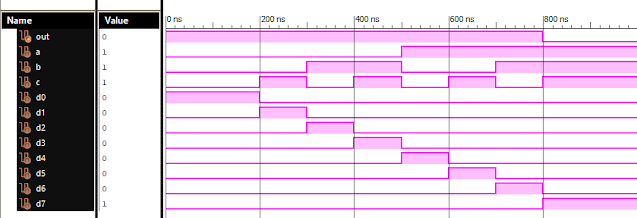
Verilog Code for 8 to 1 Multiplexer Dataflow Modelling module mux_8to1( input a, input b, input c, input D0, input D1, input D2, input D3, input D4, input D5, input D6, input D7, output out, ); module m81( output out, input D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, S0, S1, S2); assign S1bar=~S1; assign S0bar=~S0; assign S2bar=~S2; assign out = (D0 & S2bar & S1bar & S0bar) | (D1 & S2bar & S1bar & S0) | (D2 & S2bar & S1 & S0bar) + (D3 & S2bar & S1 & S0) + (D4 & S2 & S1bar & S0bar) + (D5 & S2 & S1bar & S0) + (D6 & S2 & S1 & S0bar) + (D7 & S2 & S1 & S0); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a= 0;b = 0;c = 0;D0 = 1;D1 = 0;D2 = 0;D3 = 0;D4 = 0;D5 = 0;D6 = 0;D7 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a = 0;b = 0;c = 1;d0 = ...
VLSI: 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
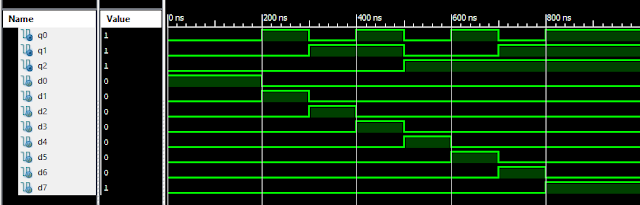
Verilog Code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling module encoder_8_to_3( input d0, input d1, input d2, input d3, input d4, input d5, input d6, input d7, output q0, output q1, output q2 ); assign q0 = ( d1 | d3 | d5 | d7 ); assign q1 = ( d2 | d3 | d6 | d7 ); assign q2 = ( d4 | d6 | d5 | d7 ); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling initial begin ...
VLSI: 1-4 DEMUX (Demultiplexer) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_4( input d, input s0, input s1, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3 ); assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s0n = ~ s0; assign y0 = d& s0n & s1n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs ...
Verilog: 2 - 4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling 2-4 Line Decoder module decoder_2_to_4( input a0, input a1, output d0, output d1, output d2, output d3 ); not (an0,a0),(an1,a1); and (d0,an0,an1),(d1,a0,an1),(d2,an0,a1),(d3,a0,a1); endmodule //Testbench code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a0 = 0;a1 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a0=1;a1=0; #100; a0=0;a1=1; #100; a0=1;a1=1; end Output: Verilog 2-4 Decoder Response Other Verilog Programs: Go to Index of Verilog Prog...
Verilog: 1to 8 DeMultiplexer (1-8 DEMUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
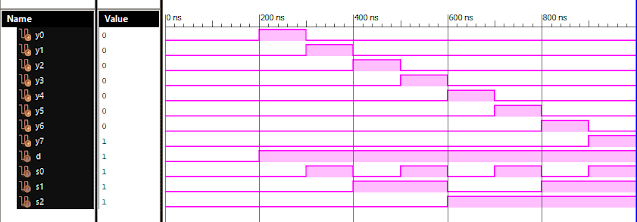
Verilog Code for 1 to 8 DeMultiplexer Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_8( input d, input s0, input s1, input s2, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3, output y4, output y5, output y6, output y7 ); assign s0n = ~ s0; assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s2n = ~ s2; assign y0 = d & s0n & s1n & s2n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n & s2n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1 & s2n; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1 & s2n; assign y4 = d & s0n & s1n & s2; assign y5 = d & s0 & s1n & s2; assign y6 = d & s0n & s1 & s2; assign y7 = d & s0 & s1 & s2; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-8 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs d = 0;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 1; ...


Comments
Post a Comment