Latest Post
Space Facts: Part 4 - Celestial Dust, Kepler 289
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
1. What is Celestial Dust:
Cluster of galaxy: Abell 1698,
A1698-ZD1 galaxy in galaxy cluster of Abel 1698 is full of space dust. Dust is made up of Silicon, Iron, Oxygen, Magnesium, Carbon, etc. Elements and dust are formed in stars by nuclear processes from gases like Helium and Hydrogen. When star dies dust and gases are emitted. So dust was formed only after bigbang happened.
2. Kepler 289 Star:
PH3c (Kepler 289c) is a dwarf planet discovered in solar system of PH3 star. PH3c planet has irregular revolution time due to external gravitational force from other planets affecting the planet's revolution. Other planets of that solar-system are PH3b (Kepler 289b) and PH3d (Kelper 289d).
PH3b and PH3d planets are very massive in size as compared to PHc so they pull the planets towards themselves when PH3 passes near them, changing the revolution orbit of PH3c. Astronomers estimate that after millions of years PH3c will be removed outside solar system by gravity-pull of the two massive planets and PH3c will become an Exoplanet.
3. Other Facts:
US708 is the fastest star discovered ever with speed of 1200 Km/sec.
Vales Marines canyon of Mars is 4500 Km long.
Ceres and Vesta are dwarf planets found in Asteroid belt of our solar system between orbit of Mars and Jupiter.
Arsia Mons and Olympus Mons are volcanoes of Mars. Olympus Mons is largest volcano of our solar-system. Largest volcano on earth is Mauna Loa in Hawaii.
Abell 1698
Astronomy
Celestial Dust
Ceres
Fastest Star
Galaxy
Kelper
Kepler
Mauna Loa
Olympus Mons
Space
Star
Vales Marines
Vesta
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular posts from this blog
Verilog: 8 to 1 Multiplexer (8-1 MUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
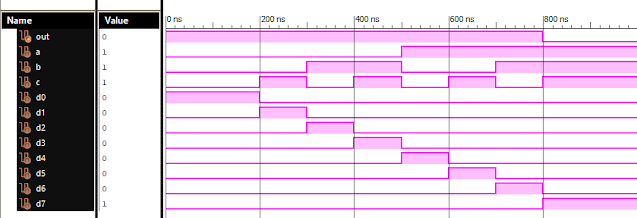
Verilog Code for 8 to 1 Multiplexer Dataflow Modelling module mux_8to1( input a, input b, input c, input D0, input D1, input D2, input D3, input D4, input D5, input D6, input D7, output out, ); module m81( output out, input D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, S0, S1, S2); assign S1bar=~S1; assign S0bar=~S0; assign S2bar=~S2; assign out = (D0 & S2bar & S1bar & S0bar) | (D1 & S2bar & S1bar & S0) | (D2 & S2bar & S1 & S0bar) + (D3 & S2bar & S1 & S0) + (D4 & S2 & S1bar & S0bar) + (D5 & S2 & S1bar & S0) + (D6 & S2 & S1 & S0bar) + (D7 & S2 & S1 & S0); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a= 0;b = 0;c = 0;D0 = 1;D1 = 0;D2 = 0;D3 = 0;D4 = 0;D5 = 0;D6 = 0;D7 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a = 0;b = 0;c = 1;d0 = ...
VLSI: 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
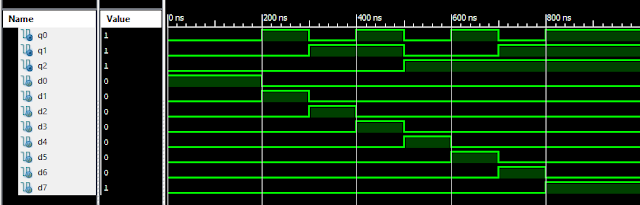
Verilog Code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling module encoder_8_to_3( input d0, input d1, input d2, input d3, input d4, input d5, input d6, input d7, output q0, output q1, output q2 ); assign q0 = ( d1 | d3 | d5 | d7 ); assign q1 = ( d2 | d3 | d6 | d7 ); assign q2 = ( d4 | d6 | d5 | d7 ); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling initial begin ...
VLSI: 1-4 DEMUX (Demultiplexer) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_4( input d, input s0, input s1, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3 ); assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s0n = ~ s0; assign y0 = d& s0n & s1n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs ...
Verilog: 2 - 4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling 2-4 Line Decoder module decoder_2_to_4( input a0, input a1, output d0, output d1, output d2, output d3 ); not (an0,a0),(an1,a1); and (d0,an0,an1),(d1,a0,an1),(d2,an0,a1),(d3,a0,a1); endmodule //Testbench code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a0 = 0;a1 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a0=1;a1=0; #100; a0=0;a1=1; #100; a0=1;a1=1; end Output: Verilog 2-4 Decoder Response Other Verilog Programs: Go to Index of Verilog Prog...
Verilog: 1to 8 DeMultiplexer (1-8 DEMUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
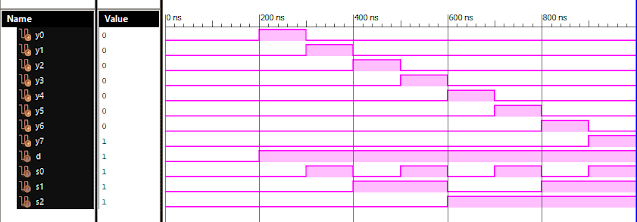
Verilog Code for 1 to 8 DeMultiplexer Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_8( input d, input s0, input s1, input s2, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3, output y4, output y5, output y6, output y7 ); assign s0n = ~ s0; assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s2n = ~ s2; assign y0 = d & s0n & s1n & s2n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n & s2n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1 & s2n; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1 & s2n; assign y4 = d & s0n & s1n & s2; assign y5 = d & s0 & s1n & s2; assign y6 = d & s0n & s1 & s2; assign y7 = d & s0 & s1 & s2; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-8 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs d = 0;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 1; ...


Comments
Post a Comment