Latest Post
International Space Station: A Space Tour
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
ISS or International Space Station is a space-station orbiting Earth 400 Km above the sea level with speed 27000 Km/hr. It is a joint project of countries like USA, Russia, Japan, ESA and CSA. ISS completes one revolution around Earth in just 93 minutes. That means in 24 hours it takes 15 revolutions.
Weight: 400 tons
Breath: 109 m
Length: 73 m
ISS is divided in 2 parts, American Orbital Segment (USOS) and Russian Orbital Segment (ROS).
Let's take a look at different modules of ISS:
1. Destiny:
Destiny module is built by NASA. It is used for experiments and taking photos from 151 cm window.
2. Quest:
Quest module is constructed by NASA. Quest contains Airlock system, and is used for spacewalks. Quest also houses spacewalk devices and spacesuits, also used as resting place for Astronauts.
3. Peer and Poshk:
It ia a Russian docking module. This module contains 2 docking facility and auto fuel transfer facility. Soyuz and Progros spacecrafts are docked to this module.
4. Kibo:
Kibo is biggest module of ISS developed by JAXA. Kibo is used for astronomy, biology, earth survey, developing new materials, biotechnology,etc. Kibo also has integrated X-RAY telescope. It's also provides facility to study plants and fish species.
5. Tranvility:
This module is developed by NASA. It contains life support systems and 6 berths. Tranvility is connected with Kupolo module from one side.
6. Zavezda:
Zavezda is a Russian module. It can be used as resting place for Astronauts. It can support 6 Astronauts in one module. Engines to give thrust to ISS are connected in Zavezda, as it is back module of ISS.
7. Columbus:
Columbus is developed by ESA. It contains laboratory for Genetics, Biology, Quantum Physics and Cosmology.
8. Kupolo:
Kupolo is developed by ESA, having 7 windows and facility to connect with other spacecraft. It has one robotic workstation and 80 cm window.
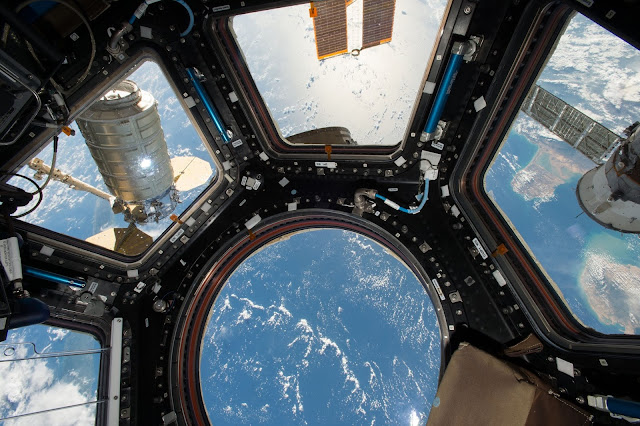 |
| Space View from Kupolo ISS |
9. Harmony:
Harmony is built by NASA. Harmony contains 4 racks providing electric supply to space-station. Kibo and Columbus are connected with Harmony.
10. Zarya:
Zarya is Russian module used for storage purpose. Technically it acts as Cargo block. It weighs 19 tons and is connected with Unity module.
11. Unity:
Unity is NASA's first module. It provides life support systems, electric supply and resting place for Astronauts. This module has more than 60,000 mechanical items. Unity weighs 12 tons and has docking facility.
Popular posts from this blog
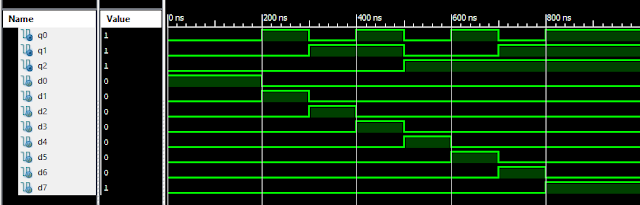
VLSI: 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling module encoder_8_to_3( input d0, input d1, input d2, input d3, input d4, input d5, input d6, input d7, output q0, output q1, output q2 ); assign q0 = ( d1 | d3 | d5 | d7 ); assign q1 = ( d2 | d3 | d6 | d7 ); assign q2 = ( d4 | d6 | d5 | d7 ); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling initial begin ...
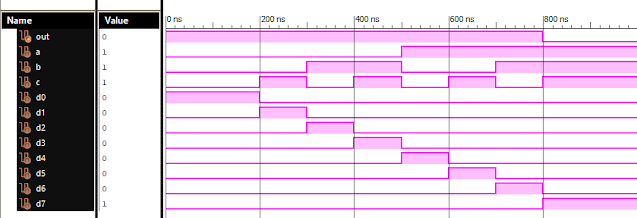
Verilog: 8 to 1 Multiplexer (8-1 MUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
Verilog Code for 8 to 1 Multiplexer Dataflow Modelling module mux_8to1( input a, input b, input c, input D0, input D1, input D2, input D3, input D4, input D5, input D6, input D7, output out, ); module m81( output out, input D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, S0, S1, S2); assign S1bar=~S1; assign S0bar=~S0; assign S2bar=~S2; assign out = (D0 & S2bar & S1bar & S0bar) | (D1 & S2bar & S1bar & S0) | (D2 & S2bar & S1 & S0bar) + (D3 & S2bar & S1 & S0) + (D4 & S2 & S1bar & S0bar) + (D5 & S2 & S1bar & S0) + (D6 & S2 & S1 & S0bar) + (D7 & S2 & S1 & S0); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a= 0;b = 0;c = 0;D0 = 1;D1 = 0;D2 = 0;D3 = 0;D4 = 0;D5 = 0;D6 = 0;D7 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a = 0;b = 0;c = 1;d0 = ...
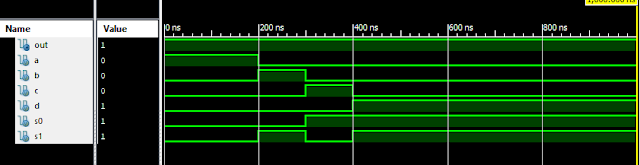
VLSI: 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling module m41(out, i0, i1, i2, i3, s0, s1); output out; input i0, i1, i2, i3, s0, s1; assign y0 = (i0 & (~s0) & (~s1)); assign y1 = (i1 & (~s0) & s1); assign y2 = (i2 & s0 & (~s1)); assign y3 = (i3 & s0 & s1); assign out = (y0 | y1 | y2 | y3); endmodule //Testbench code for 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a = 1;b = 0;c = 0;d = 0;s0 = 0;s1 = 0; ...
VLSI: 1-4 DEMUX (Demultiplexer) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_4( input d, input s0, input s1, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3 ); assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s0n = ~ s0; assign y0 = d& s0n & s1n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs ...
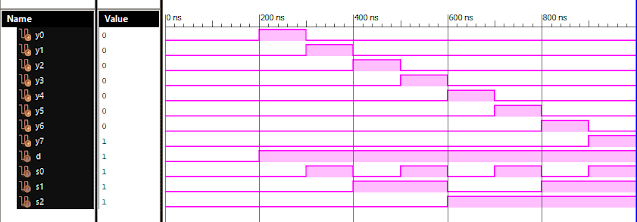
Verilog: 1to 8 DeMultiplexer (1-8 DEMUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
Verilog Code for 1 to 8 DeMultiplexer Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_8( input d, input s0, input s1, input s2, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3, output y4, output y5, output y6, output y7 ); assign s0n = ~ s0; assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s2n = ~ s2; assign y0 = d & s0n & s1n & s2n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n & s2n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1 & s2n; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1 & s2n; assign y4 = d & s0n & s1n & s2; assign y5 = d & s0 & s1n & s2; assign y6 = d & s0n & s1 & s2; assign y7 = d & s0 & s1 & s2; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-8 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs d = 0;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 1; ...

Comments
Post a Comment