Posts
Showing posts from March, 2020
Latest Post
Pressure Converter
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Pressure Equivalents First, type the number you wish converted here: Then, click radio buttons for desired conversion: Fm: megadynes/ sq cm kg/ sq cm lb/ sq in atmos- pheres Hg* Meters Hg* Inches H2O* Meters H20* Inches H20* Feet To: megadynes/ sq cm kg/ sq cm lb/ sq in atmos- pheres Hg* Meters Hg* Inches H2O* Meters H2O* Inches H20* Feet *Standard columns of Mercury at 0 o C, g = 980.665 cm/sec/sec Standard columns of Water at 60 o F, g = 32.1756 ft/sec/sec
Loan Calculator
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
The results of this loan payment calculator are for comparison purposes only. They will be a close approximation of actual loan repayments if available at the terms entered, from a financial institution. To use, enter values for the Loan Amount, Number of Months for Loan, and the Interest Rate (e.g. 7.25), and click the Calculate button. Clicking the Reset button will clear entered values. Description Data Entry Loan Amount Loan Length in Months Interest Rate Monthly Payment Calculated Enter only numeric values (no commas), using decimal points where needed. Non-numeric values will cause errors.
VLSI: Half Subtractor and Full Subtractor Gate Level Modelling
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
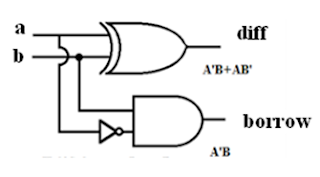
Half Subtractor: Verilog Module Code: module half_subtractor ( input a, input b, output diff output borr ); wire x; xor (diff,a,b); not (x,a); and (borr,x,b); endmodule Full Subtractor: Verilog Module Code: module full_subtractor ( input a, input b, input c, output diff output borr ); wire x,n2,z,n1; xor s1(x,a,b); not s3(n2,x); not s4(n1,c); and s5(y,n1,b); xor s2(diff,a,x); and s6(z,n2,a); or (borr,y,z); endmodule
VLSI: Logic Gates Gate Level Modelling
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
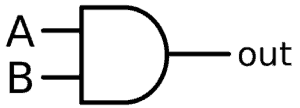
AND Gate: Verilog Module Code: module and_gate ( input a, input b, output c ); and (c,a,b); endmodule OR Gate: Verilog Module Code: module or_gate ( input a, input b, output c ); or (c,a,b); endmodule NAND Gate: Verilog Module Code: module nand_gate ( input a, input b, output c ); nand (c,a,b); endmodule NOR Gate: Verilog Module Code: module nor_gate ( input a, input b, output c ); nor (c,a,b); endmodule XOR Gate: Verilog Module Code: module xor_gate ( input a, ...
VLSI: 2 Bit Magnitude Comparator Dataflow Modelling
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
module mag_comp2bit( input a0, input a1, input b0, input b1, output p, // p = (a < b) output r, // r = (a > b) output q // q = (a = b) ); assign q = ((~a1) ^ (b1)) & (a0 & b0); assign p = (((~a1) & b1) | (b0 & (~a0) & (~a1)) | ((~a0) & b1 & b0)); assign r = ((a1 & (~b1)) | ((~b0) & a1 & a0) | (a0 & (~b1) & (~b0))); endmodule
VLSI: BCD to Excess 3 and Excess 3 to BCD Dataflow Modelling
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
module bcd_ex3_Dataflow( input a, input b, input c, input d, output w, output x, output y, output z ); assign w = (a | (b & c) | (b & d)); assign x = (((~b) & c) | ((~b) & d) | (b & (~c) & (~d))); assign y = ((c & d) | ((~c) & (~d))); assign z = ~d; endmodule Excess 3 to BCD: module ex3_to_bcd( input w, input x, input y, input z, output a, output b, output c, output d ); assign a = ((w & x) | (w & y & z)); assign b = (((~x) & (~y)) | ((~x) & (~z)) | (x & y & z)); assign c = (((~y) & z) | (y & (~z))); assign d = ~z; endmodule
VLSI: Gray to Binary and Binary to Gray Dataflow Modelling
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Gray to Binary: module Gray_to_Binary( input g1, input g2, input g3, input g4, output b1, output b2, output b3, output b4 ); assign b4 = g4; assign b3 = b4 ^ g3; assign b2 = b3 ^ g2; assign b1 = b2 ^ g1; endmodule Binary to Gray: module Binary_to_Gray( input b1, input b2, input b3, input b4, output g1, output g2, output g3, output g4 ); assign g1 = b1; assign g2 = b1 ^ b2; assign g3 = b2 ^ b3; assign g4 = b3 ^ b4; endmodule
VLSI: 4-1 Multiplexer (MUX) Dataflow Modelling
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
module Four_to_One_MUX( input s0, input s1, input i0, input i1, input i2, input i3, output out ); assign y0 = (i0 & (~s0) & (~s1)); assign y1 = (i1 & (~s0) & s1); assign y2 = (i2 & s0 & (~s1)); assign y3 = (i3 & s0 & s1); assign out = (y0 | y1 | y2 | y3); endmodule MUX using Conditional Statement: module Four_to_One_MUX( input s0, input s1, input i0, input i1, input i2, input i3, output out ); assign out = s0 ? (s1 ? i3 : i2) : (s1 ? i1 : i0); endmodule
VLSI: Half Adder and Full Adder Gate Level Modelling
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
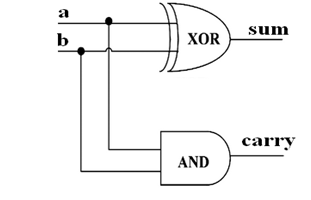
Half Adder: module HalfAdder( input A, input B, output sum, output carry ); xor (sum,A,B); and (carry,A,B); endmodule Full Adder: module FullAdder( input A, input B, input Cin, output sum, output carry ); wire a1, a2, a3; xor g1(a1,A,B); and g4(a2,A,B); and g3(a3,a1,Cin); or g5(carry,a2,a3); xor g2(sum,a1,Cin); endmodule
VLSI: Binary to Gray and Gray to Binary Converter Gate Level Modelling
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Binary to Gray: module Binary_to_Gray( input b1, input b2, input b3, input b4, output g1, output g2, output g3, output g4 ); xor u1(g2,b1,b2); xor u2(g3,b2,b3); xor u3(g4,b4,b3); buf u4(g1,b1); endmodule Gray to Binary: module GraytoBinary( input g1, input g2, input g3, input g4, output b1, output b2, output b3, output b4 ); xor u1(b4,g1,b3); xor u2(b3,g3,b2); xor u3(b2,g2,g1); buf u4(b1,g1); endmodule
VLSI: 8-1 Demultiplexer Dataflow Modelling
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
module Demultiplexer(in,s0,s1,s2,d0,d1,d2,d3,d4,d5,d6,d7); input in,s0,s1,s2; output d0,d1,d2,d3,d4,d5,d6,d7; assign d0=(in & ~s2 & ~s1 &~s0), d1=(in & ~s2 & ~s1 &s0), d2=(in & ~s2 & s1 &~s0), d3=(in & ~s2 & s1 &s0), d4=(in & s2 & ~s1 &~s0), d5=(in & s2 & ~s1 &s0), d6=(in & s2 & s1 &~s0), d7=(in & s2 & s1 &s0); endmodule
VLSI: Carry Look Ahead Adder
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
module CLA_Adder(a,b,cin,sum,cout); input [3:0] a,b; input cin; output [3:0] sum; output cout; wire p0,p1,p2,p3,g0,g1,g2,g3,c1,c2,c3,c4; assign p0=(a[0]^b[0]), p1=(a[1]^b[1]), p2=(a[2]^b[2]), p3=(a[3]^b[3]); assign g0=(a[0]&b[0]), g1=(a[1]&b[1]), g2=(a[2]&b[2]), g3=(a[3]&b[3]); assign c0=cin, c1=g0|(p0&cin), c2=g1|(p1&g0)|(p1&p0&cin), c3=g2|(p2&g1)|(p2&p1&g0)|(p1&p1&p0&cin), c4=g3|(p3&g2)|(p3&p2&g1)|(p3&p2&p1&g0)|(p3&p2&p1&p0&cin); assign sum[0]=p0^c0, sum[1]=p1^c1, sum[2]=p2^c2, sum[3]=p3^c3; assign cout=c4; endmodule
VLSI: 4 Bit Adder and 4 Bit Subtractor
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
4 Bit Adder: module MultibitAdder(a,b,cin,sum,cout); input [3:0] a,b; input cin; output [3:0]sum; output cout; assign {cout,sum}=a+b+cin; endmodule 4 Bit Subtractor: module MultibitSubstractor(a,b,bin,difference,bout); input [3:0] a,b; input bin; output [3:0]difference; output bout; assign {bout,difference}=a-b-bin; endmodule
VLSI: Logic Gates Dataflow Modelling
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

AND Gate: Verilog Module Code: module and_gate ( input a, input b, output c ); assign c = a & b; endmodule OR Gate: Verilog Module Code: module or_gate ( input a, input b, output c ); assign c = a | b; endmodule NAND Gate: Verilog Module Code: module nand_gate ( input a, input b, output c ); assign c = ~ ( a & b ); endmodule NOR Gate: Verilog Module Code: module nor_gate ( input a, input b, output c ); assign c = ~ ( a | b ); endmodule XOR Gate: Verilog Module Code: module xor_gate ( ...
Popular posts from this blog
Verilog: 8 to 1 Multiplexer (8-1 MUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
Verilog Code for 8 to 1 Multiplexer Dataflow Modelling module mux_8to1( input a, input b, input c, input D0, input D1, input D2, input D3, input D4, input D5, input D6, input D7, output out, ); module m81( output out, input D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, S0, S1, S2); assign S1bar=~S1; assign S0bar=~S0; assign S2bar=~S2; assign out = (D0 & S2bar & S1bar & S0bar) | (D1 & S2bar & S1bar & S0) | (D2 & S2bar & S1 & S0bar) + (D3 & S2bar & S1 & S0) + (D4 & S2 & S1bar & S0bar) + (D5 & S2 & S1bar & S0) + (D6 & S2 & S1 & S0bar) + (D7 & S2 & S1 & S0); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a= 0;b = 0;c = 0;D0 = 1;D1 = 0;D2 = 0;D3 = 0;D4 = 0;D5 = 0;D6 = 0;D7 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a = 0;b = 0;c = 1;d0 = ...
VLSI: 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling module encoder_8_to_3( input d0, input d1, input d2, input d3, input d4, input d5, input d6, input d7, output q0, output q1, output q2 ); assign q0 = ( d1 | d3 | d5 | d7 ); assign q1 = ( d2 | d3 | d6 | d7 ); assign q2 = ( d4 | d6 | d5 | d7 ); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling initial begin ...
VLSI: 1-4 DEMUX (Demultiplexer) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_4( input d, input s0, input s1, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3 ); assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s0n = ~ s0; assign y0 = d& s0n & s1n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs ...
VLSI: 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling module m41(out, i0, i1, i2, i3, s0, s1); output out; input i0, i1, i2, i3, s0, s1; assign y0 = (i0 & (~s0) & (~s1)); assign y1 = (i1 & (~s0) & s1); assign y2 = (i2 & s0 & (~s1)); assign y3 = (i3 & s0 & s1); assign out = (y0 | y1 | y2 | y3); endmodule //Testbench code for 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a = 1;b = 0;c = 0;d = 0;s0 = 0;s1 = 0; ...
Verilog: 2 - 4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling 2-4 Line Decoder module decoder_2_to_4( input a0, input a1, output d0, output d1, output d2, output d3 ); not (an0,a0),(an1,a1); and (d0,an0,an1),(d1,a0,an1),(d2,an0,a1),(d3,a0,a1); endmodule //Testbench code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a0 = 0;a1 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a0=1;a1=0; #100; a0=0;a1=1; #100; a0=1;a1=1; end Output: Verilog 2-4 Decoder Response Other Verilog Programs: Go to Index of Verilog Prog...