Posts
Showing posts from November, 2020
Latest Post
Verilog: 3 to 8 Decoder Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement with Testbench Code
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

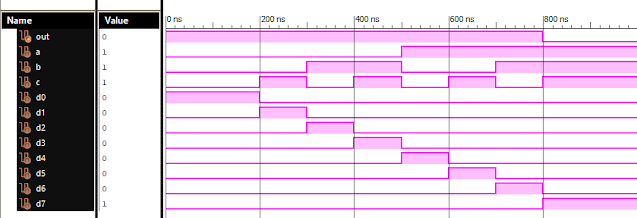
Verilog Code for 3 to 8 Decoder Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement with Testbench Code module 3_8_DEC( input [3:0]din, output [7:0]dout ); reg [7:0]dout; always @ (din) case (din) 0 : dout[0] = 1; 1 : dout[1] = 1; 2 : dout[2] = 1; 3 : dout[3] = 1; 4 : dout[4] = 1; 5 : dout[5] = 1; 6 : dout[6] = 1; 7 : dout[7] = 1; default : dout = 8’bxxxxxxxx; endcase endmodule //Testbench code for 3 to 8 Decoder Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement initial begin // Initialize Inputs din = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; din=0; #100; din=1; #100; din=2; #100; din=3; #100; din=4; #100; din=5; #100; din=6;...
Verilog: 8 to 1 MUX Behavioral Modelling using Verilog Case Statement with Testbench Code
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

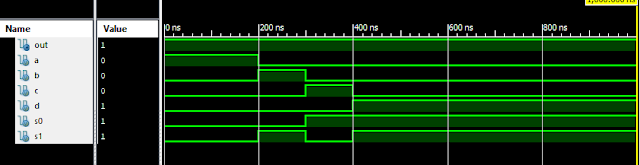
Verilog Code for 8 to 1 MUX Behavioral Modelling using Verilog Case Statement with Testbench Code module 8_1_MUX( input [7:0]i, input s2,s1,s0, output out ); reg out; always @ (i or s2 or s1 or s0) case ({s2,s1,s0}) 0 : out = I[0]; 1 : out = I[1]; 2 : out = I[2]; 3 : out = I[3]; 4 : out = I[4]; 5 : out = I[5]; 6 : out = I[6]; 7 : out = I[7]; default : out = 1’bx; endcase endmodule //Testbench code for 8 to 1 MUX (Multiplexer) Behavioral Modelling using Verilog Case Statement initial begin // Initialize Inputs i=8’b 10101010; s2=0; s1=0; s0=0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; s2=0; s1=0; s0=1; #100; s2=0;...
Verilog: 1 to 4 DEMUX (Demultiplexer) Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement with Testbench Code
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Verilog Code for 1 to 4 DEMUX Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement with Testbench Code module 1_4_DEMUX( input i, input s1, s0, output [3:0]out ); reg [3:0]out; always @ (i or s0 or s1) case ({s1,s0}) 0: out0 = i; 1: out1 = i; 2: out2 = i; 3: out3 = i; default: out = 4'bxxxx; endcase endmodule //Testbench code for 1 to 4 DEMUX (DeMultiplexer) Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement initial begin // Initialize Inputs i = 1;s1 = 0;s0 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; s1=0; s0=1; #100; s1=1; s0=0; #100; s1=1; s0=1; end initial begin #100 ; $monitor (“I=%b, s1=%b, s0=%b, out=%b”, I, s1, s0, out); end endmodule
Verilog: 1 to 8 DEMUX Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement with Testbench Code
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Verilog Code for 1 to 8 DEMUX Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement with Testbench Code module 1_8_DEMUX( input i, input s2, s1, s0, output [7:0]out ); reg [7:0]out; always @ (i or s0 or s1 or s2) case ({s2,s1,s0}) 0: out0 = i; 1: out1 = i; 2: out2 = i; 3: out3 = i; 4: out4 = i; 5: out5 = i; 6: out6 = i; 7: out7 = i; default: out = 8'bxxxxxxx; endcase endmodule //Testbench code for 1 to 8 DEMUX (DeMultiplexer) Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement initial begin // Initialize Inputs i = 1;s2 = 0;s1 = 0;s0 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; s2=0; s1=0; s0=1; #100; s2=0; s1=1; s0=0; #100; s2=0; s1=1; s0=1; #100; s2=1; s1=0; s0=0; #100; s2=1; s1=0; s0=1;...
Verilog: 1-2 De-Multiplexer (DEMUX) using Case Statement Behavioral Modelling with Testbench Code
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
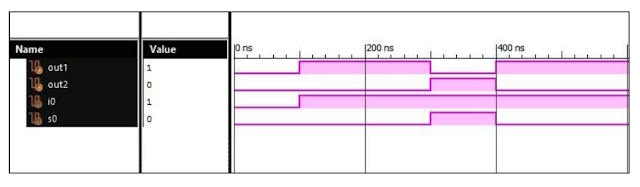
Verilog Code for 1 to 2 DEMUX Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement with Testbench Code module 1_2_DEMUX( input i0, input s0, output out1, output out2 ); always @ (i0 or s0) case (s0) 0: out1 = i0; 1: out2 = i0; default: out1 = 1'bx;out2 = 1'bx; endcase endmodule //Testbench code for 1 to 2 DEMUX (DeMultiplexer) Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement initial begin // Initialize Inputs i0 = 1;s0 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; s0 = 1; #100; s0 = 0; end Output: 1-2 DeMUX Response
Verilog: 2-1 Multiplexer with Case Statement Behavioral Modelling with Testbench Code
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
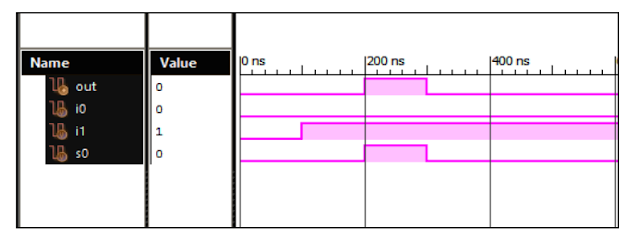
Verilog Code for 2 to 1 MUX Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement with Testbench Code module 2_1_MUX( input i0, input i1, input s0, output out ); always @ (i0 or i1 or s0) case (s0) 0: out = i0; 1: out = i1; default: out = 1'bx; endcase endmodule //Testbench code for 2 to 1 MUX (Multiplexer)Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement initial begin // Initialize Inputs i0 = 1;i1 = 1;s0 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; s0 = 0; #100; s0 = 1; end Output: 2 - 1 MUX Behavioral Modelling Response
Verilog: 4 to 1 Multiplexer Behavioral Modelling with Testbench Code
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Verilog Code 4-1 Multiplexer Behavioral Modelling using Case Statement module Mux_4to1 ( input [3:0] i, input s1, s0, output out ); always @(i or s1 or s0) case({s1, s0}) 0 : out = i[0]; 1 : out = i[1]; 2 : out = i[2]; 3 : out = i[3]; default : out = 1’bx; endcase endmodule // test-bench initial begin i=1'b1010; s1=0; s0=0; #100; //wait 100ns for global reset to finish //add stimulus here #100 s1 = 0; s0= 1; #100 s1 = 1; s0= 0; #100 s1 = 1; s0= 1; end
Popular posts from this blog
Verilog: 8 to 1 Multiplexer (8-1 MUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
Verilog Code for 8 to 1 Multiplexer Dataflow Modelling module mux_8to1( input a, input b, input c, input D0, input D1, input D2, input D3, input D4, input D5, input D6, input D7, output out, ); module m81( output out, input D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, S0, S1, S2); assign S1bar=~S1; assign S0bar=~S0; assign S2bar=~S2; assign out = (D0 & S2bar & S1bar & S0bar) | (D1 & S2bar & S1bar & S0) | (D2 & S2bar & S1 & S0bar) + (D3 & S2bar & S1 & S0) + (D4 & S2 & S1bar & S0bar) + (D5 & S2 & S1bar & S0) + (D6 & S2 & S1 & S0bar) + (D7 & S2 & S1 & S0); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a= 0;b = 0;c = 0;D0 = 1;D1 = 0;D2 = 0;D3 = 0;D4 = 0;D5 = 0;D6 = 0;D7 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a = 0;b = 0;c = 1;d0 = ...
VLSI: 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
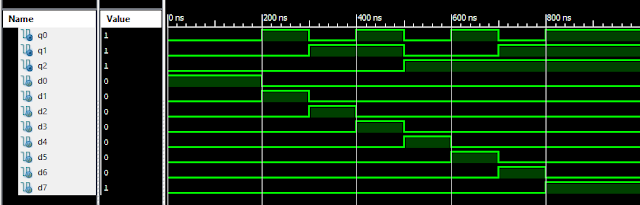
Verilog Code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling module encoder_8_to_3( input d0, input d1, input d2, input d3, input d4, input d5, input d6, input d7, output q0, output q1, output q2 ); assign q0 = ( d1 | d3 | d5 | d7 ); assign q1 = ( d2 | d3 | d6 | d7 ); assign q2 = ( d4 | d6 | d5 | d7 ); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling initial begin ...
VLSI: 1-4 DEMUX (Demultiplexer) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_4( input d, input s0, input s1, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3 ); assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s0n = ~ s0; assign y0 = d& s0n & s1n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs ...
Verilog: 2 - 4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling 2-4 Line Decoder module decoder_2_to_4( input a0, input a1, output d0, output d1, output d2, output d3 ); not (an0,a0),(an1,a1); and (d0,an0,an1),(d1,a0,an1),(d2,an0,a1),(d3,a0,a1); endmodule //Testbench code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a0 = 0;a1 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a0=1;a1=0; #100; a0=0;a1=1; #100; a0=1;a1=1; end Output: Verilog 2-4 Decoder Response Other Verilog Programs: Go to Index of Verilog Prog...
VLSI: 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling module m41(out, i0, i1, i2, i3, s0, s1); output out; input i0, i1, i2, i3, s0, s1; assign y0 = (i0 & (~s0) & (~s1)); assign y1 = (i1 & (~s0) & s1); assign y2 = (i2 & s0 & (~s1)); assign y3 = (i3 & s0 & s1); assign out = (y0 | y1 | y2 | y3); endmodule //Testbench code for 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a = 1;b = 0;c = 0;d = 0;s0 = 0;s1 = 0; ...