Posts
Showing posts from 2022
Latest Post
Samir Palnitkar Solution Manual Free Download PDF of Verilog HDL
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

This is a solution guide to the exercises of the book "The Solution Manual of the Verilog HDL: A Guide to Digital Design and Synthesis by Samir Palnitkar". Following are the Solutions to Solution Manual on Verilog HDL: A Guide to Digital Design and Synthesis by Samir Palnitkar , exercises of all chapters in the book. Chapter 1 ----------------- No Exercises ---------------- Chapter 2 : Hierarchical Modeling Concepts Chapter 3 : Basic Concepts Chapter 4 : Modules and Ports Chapter 5: Gate-level Modeling Chapter 6 : Dataflow Modeling Chapter 7 : Behavioral Modeling Chapter 8 : Tasks and Functions Download Solution Manual: Click on this link (Mega.nz Link) [Solution Manual to Verilog HDL: A Guide to Digital Design and Synthesis by Samir Palnitkar] Preview of Solution Manual: For Verilog Programs: Go to Index of Verilog Programming Tags: Verilog HDL solutio...
Verilog: VLSI Code for D Flip Flop with Testbench Dataflow Modelling
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
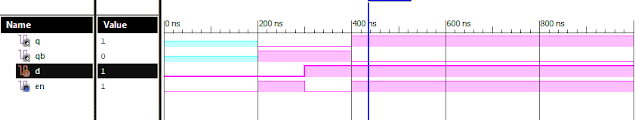
Verilog Code for D Flip Flop Dataflow Modelling module DFF( input d, input en, output q, output qb ); assign a = ( en & ( ~ d )); assign b = ( en & d ); assign q = ~ ( a | qb ); assign qb = ~ ( b | q ); endmodule //Testbench initial begin // Initialize Inputs d = 0; en = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100;d = 0;en = 1; #100;d = 1;en = 0; #100;d = 1;en = 1; end Xillinx Output: D Flip Flop Dataflow Modelling Also See: List of Verilog Programs
Verilog: VLSI Code for T Flip Flop Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
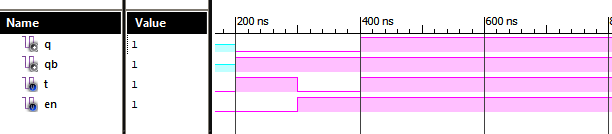
Verilog Code for T Flip Flop Dataflow Modelling module TFF( input t, input en, output q, output qb ); assign a = ~ ( qb & t & en ); assign b = ~ ( q & t & en ); assign q = ~ ( qb & a ); assign qb = ~ ( b & q & ( ~ t ) ); endmodule //Testbench initial begin // Initialize Inputs t = 0; en = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100;t = 1;en = 0; #100;t = 0;en = 1; #100;t = 1;en = 1; end Xillinx Output: T Flip Flop Dataflow Modelling Also See: List of Verilog Programs
Verilog: 1 Bit Magnutude Comparator Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
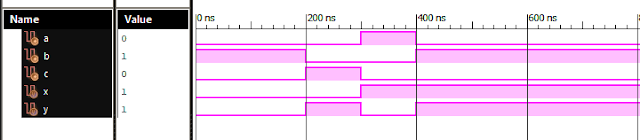
Verilog Code for 1 Bit Magnitude Comparator Dataflow Modelling module comparator_1_bit( input x, input y, output a, //x>y output b, //x=y output c //x<y ); assign xn = ~ x; assign yn = ~ y; assign a = x & yn; assign c = xn & y; assign b = ~ ( a | c ); endmodule //Testbench initial begin // Initialize Inputs x = 0;y = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; x=0;y=1; #100; x=1;y=0; #100; x=1;y=1; end Xillinx Output: 1 Bit Magnitude Comparator Dataflow Modelling Also See: List of Verilog Programs
Verilog: 1 to 2 DeMultiplexer (1-2 DEMUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
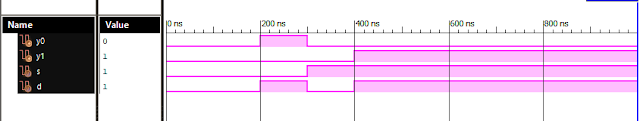
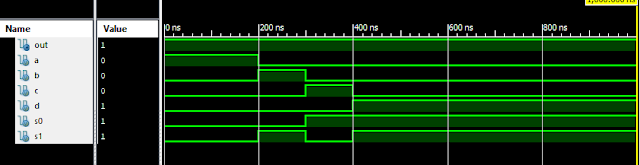
Verilog Code for 1 to 2 DeMultiplexer Dataflow Modelling module DEMUX_1_to_2( input s, input d, output y0, output y1 ); assign sn = ~ s; assign y0 = sn & d; assign y1 = s & d; endmodule //Testbench initial begin // Initialize Inputs s = 0; d = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; s=0;d=1; #100; s=1;d=0; #100; s=1;d=1; end Xillinx Output: 1-2 DEMUX Verilog Coding Also See: List of Verilog Programs
Verilog: 8 to 1 Multiplexer (8-1 MUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
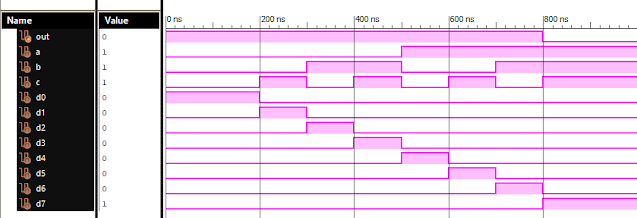
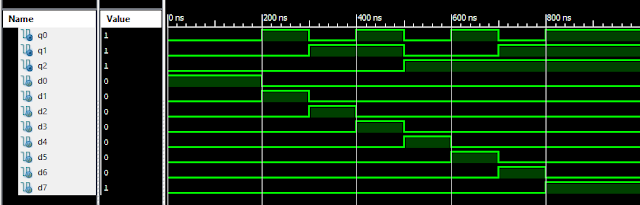
Verilog Code for 8 to 1 Multiplexer Dataflow Modelling module mux_8to1( input a, input b, input c, input D0, input D1, input D2, input D3, input D4, input D5, input D6, input D7, output out, ); module m81( output out, input D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, S0, S1, S2); assign S1bar=~S1; assign S0bar=~S0; assign S2bar=~S2; assign out = (D0 & S2bar & S1bar & S0bar) | (D1 & S2bar & S1bar & S0) | (D2 & S2bar & S1 & S0bar) + (D3 & S2bar & S1 & S0) + (D4 & S2 & S1bar & S0bar) + (D5 & S2 & S1bar & S0) + (D6 & S2 & S1 & S0bar) + (D7 & S2 & S1 & S0); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a= 0;b = 0;c = 0;D0 = 1;D1 = 0;D2 = 0;D3 = 0;D4 = 0;D5 = 0;D6 = 0;D7 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a = 0;b = 0;c = 1;d0 = ...
Popular posts from this blog
Verilog: 8 to 1 Multiplexer (8-1 MUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
Verilog Code for 8 to 1 Multiplexer Dataflow Modelling module mux_8to1( input a, input b, input c, input D0, input D1, input D2, input D3, input D4, input D5, input D6, input D7, output out, ); module m81( output out, input D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, S0, S1, S2); assign S1bar=~S1; assign S0bar=~S0; assign S2bar=~S2; assign out = (D0 & S2bar & S1bar & S0bar) | (D1 & S2bar & S1bar & S0) | (D2 & S2bar & S1 & S0bar) + (D3 & S2bar & S1 & S0) + (D4 & S2 & S1bar & S0bar) + (D5 & S2 & S1bar & S0) + (D6 & S2 & S1 & S0bar) + (D7 & S2 & S1 & S0); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a= 0;b = 0;c = 0;D0 = 1;D1 = 0;D2 = 0;D3 = 0;D4 = 0;D5 = 0;D6 = 0;D7 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a = 0;b = 0;c = 1;d0 = ...
VLSI: 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling module encoder_8_to_3( input d0, input d1, input d2, input d3, input d4, input d5, input d6, input d7, output q0, output q1, output q2 ); assign q0 = ( d1 | d3 | d5 | d7 ); assign q1 = ( d2 | d3 | d6 | d7 ); assign q2 = ( d4 | d6 | d5 | d7 ); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling initial begin ...
VLSI: 1-4 DEMUX (Demultiplexer) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_4( input d, input s0, input s1, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3 ); assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s0n = ~ s0; assign y0 = d& s0n & s1n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs ...
VLSI: 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling module m41(out, i0, i1, i2, i3, s0, s1); output out; input i0, i1, i2, i3, s0, s1; assign y0 = (i0 & (~s0) & (~s1)); assign y1 = (i1 & (~s0) & s1); assign y2 = (i2 & s0 & (~s1)); assign y3 = (i3 & s0 & s1); assign out = (y0 | y1 | y2 | y3); endmodule //Testbench code for 4-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a = 1;b = 0;c = 0;d = 0;s0 = 0;s1 = 0; ...
Verilog: 2 - 4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling 2-4 Line Decoder module decoder_2_to_4( input a0, input a1, output d0, output d1, output d2, output d3 ); not (an0,a0),(an1,a1); and (d0,an0,an1),(d1,a0,an1),(d2,an0,a1),(d3,a0,a1); endmodule //Testbench code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a0 = 0;a1 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a0=1;a1=0; #100; a0=0;a1=1; #100; a0=1;a1=1; end Output: Verilog 2-4 Decoder Response Other Verilog Programs: Go to Index of Verilog Prog...