Latest Post
Applied Instrumentation GTU (Sem-1) - ME Instrumentation and Control (IC)
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
1. STUDY MATERIAL for Applied Instrumentation GTU (Sem-1) - ME Instrumentation and Control (IC)
- SEM 1:
Subjects: AIDC (Advanced Industrial Drives and Control)
ISC (Intelligent Systems and Control)
OTE (Optimization Techniques for Engineers)
ESI (Embedded System for Instrumentation)
IPR
Click on the below given links to download study material:
Syllabus
Books
Notes
Study Material
Lab Manual
Question Papers
Assignments
Sem 2: ME - Applied Instrumentation
Click on the below given link to download study material:
Subjects:
AVD (Advanced Verilog Design)
ISI (Intelligent Sensors and Instrumentation)
DC (Digital Control)
ASPE (Advanced Signal Processing and Estimation)
Disaster Management
Also See:
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular posts from this blog
Verilog: 8 to 1 Multiplexer (8-1 MUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
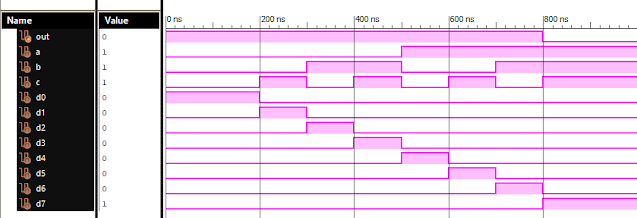
Verilog Code for 8 to 1 Multiplexer Dataflow Modelling module mux_8to1( input a, input b, input c, input D0, input D1, input D2, input D3, input D4, input D5, input D6, input D7, output out, ); module m81( output out, input D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, S0, S1, S2); assign S1bar=~S1; assign S0bar=~S0; assign S2bar=~S2; assign out = (D0 & S2bar & S1bar & S0bar) | (D1 & S2bar & S1bar & S0) | (D2 & S2bar & S1 & S0bar) + (D3 & S2bar & S1 & S0) + (D4 & S2 & S1bar & S0bar) + (D5 & S2 & S1bar & S0) + (D6 & S2 & S1 & S0bar) + (D7 & S2 & S1 & S0); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a= 0;b = 0;c = 0;D0 = 1;D1 = 0;D2 = 0;D3 = 0;D4 = 0;D5 = 0;D6 = 0;D7 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a = 0;b = 0;c = 1;d0 = ...
VLSI: 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
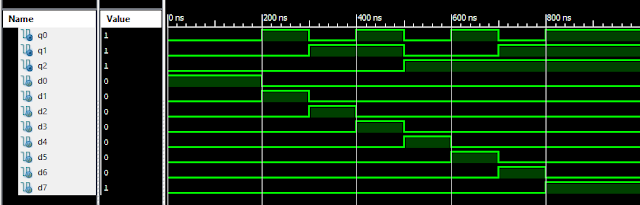
Verilog Code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling module encoder_8_to_3( input d0, input d1, input d2, input d3, input d4, input d5, input d6, input d7, output q0, output q1, output q2 ); assign q0 = ( d1 | d3 | d5 | d7 ); assign q1 = ( d2 | d3 | d6 | d7 ); assign q2 = ( d4 | d6 | d5 | d7 ); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling initial begin ...
VLSI: 1-4 DEMUX (Demultiplexer) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_4( input d, input s0, input s1, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3 ); assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s0n = ~ s0; assign y0 = d& s0n & s1n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs ...
Verilog: 2 - 4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling 2-4 Line Decoder module decoder_2_to_4( input a0, input a1, output d0, output d1, output d2, output d3 ); not (an0,a0),(an1,a1); and (d0,an0,an1),(d1,a0,an1),(d2,an0,a1),(d3,a0,a1); endmodule //Testbench code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a0 = 0;a1 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a0=1;a1=0; #100; a0=0;a1=1; #100; a0=1;a1=1; end Output: Verilog 2-4 Decoder Response Other Verilog Programs: Go to Index of Verilog Prog...
Verilog: 1to 8 DeMultiplexer (1-8 DEMUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
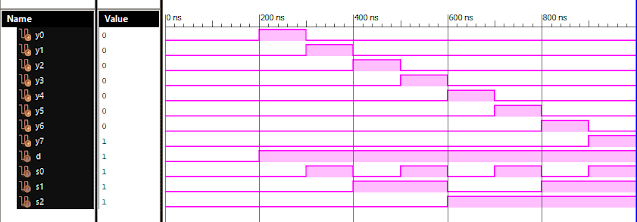
Verilog Code for 1 to 8 DeMultiplexer Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_8( input d, input s0, input s1, input s2, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3, output y4, output y5, output y6, output y7 ); assign s0n = ~ s0; assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s2n = ~ s2; assign y0 = d & s0n & s1n & s2n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n & s2n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1 & s2n; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1 & s2n; assign y4 = d & s0n & s1n & s2; assign y5 = d & s0 & s1n & s2; assign y6 = d & s0n & s1 & s2; assign y7 = d & s0 & s1 & s2; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-8 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs d = 0;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 1; ...


Comments
Post a Comment