Posts
Showing posts from February, 2020
Latest Post
C Program for Level Sketch
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
C Level Sketch: #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<math.h> int main() { float th,ov, HH,H,L,LL,lowTap,UpTap,CC,HH1,H1,L1,LL1,HHper,Hper,Lper,LLper,BtTap; char ch; do { printf("\nEnter Tank Height in mm:"); scanf("%f",&th); printf("\nHeight of HH:"); scanf("%f",&HH); printf("\nHeight of H:"); scanf("%f",&H); printf("\nHeight of L:"); scanf("%f",&L); printf("\nHeight of LL:"); scanf("%f",&LL); printf("\nEnter Height of Overflow Nozzle (if required):"); scanf("%f",&ov); if (ov != 0) { th = ov; } else { th = th; } printf("Height Valid: %.2f",th); HHper = (HH * 100)/th; Hper = (H * 100)/th; Lper = (L * 100)/th; LLper = (LL * 100)/th; if (HHper < 90 && LLper > 10) { ...
Sun - The Ball of Fire
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Mysterious Sun: Electromagnetic winds emmited from Sun are solar winds. Solar winds consists of protons and electrons, when these protons and electrons interact with Earth's magnetic field sky get lit up by different colors. The solar winds are emmited by solar holes in sun, as these solar holes are less dense than other parts of Sun, they provide path to allow the wind outwards to surface of Sun. These winds are thrown out by such a huge force that they can travel very long distances, even reaching to Earth. These winds can have speed up to 1000 Km/sec. Solar Emission Even though we know Sun from centuries, there are many mysteries of Sun remained unsolved. Most popular mystery is regarding Corona of Sun. Corona is outer layer of Sun's atmosphere. Corona is hotter than the inner layer Chromosphere. Sun's visible surface Photosphere has temperature 5800°C. Outer layer of Photosphere is Chromosphere. Temperature of Chromosphere is estimated to be 4000°C....
Popular posts from this blog
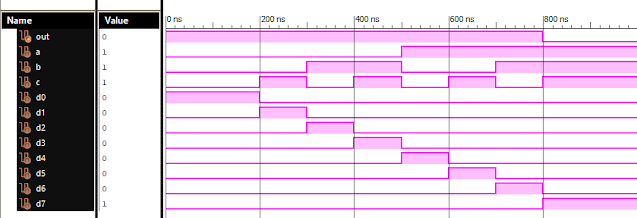
Verilog: 8 to 1 Multiplexer (8-1 MUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
Verilog Code for 8 to 1 Multiplexer Dataflow Modelling module mux_8to1( input a, input b, input c, input D0, input D1, input D2, input D3, input D4, input D5, input D6, input D7, output out, ); module m81( output out, input D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, S0, S1, S2); assign S1bar=~S1; assign S0bar=~S0; assign S2bar=~S2; assign out = (D0 & S2bar & S1bar & S0bar) | (D1 & S2bar & S1bar & S0) | (D2 & S2bar & S1 & S0bar) + (D3 & S2bar & S1 & S0) + (D4 & S2 & S1bar & S0bar) + (D5 & S2 & S1bar & S0) + (D6 & S2 & S1 & S0bar) + (D7 & S2 & S1 & S0); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-1 MUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a= 0;b = 0;c = 0;D0 = 1;D1 = 0;D2 = 0;D3 = 0;D4 = 0;D5 = 0;D6 = 0;D7 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a = 0;b = 0;c = 1;d0 = ...
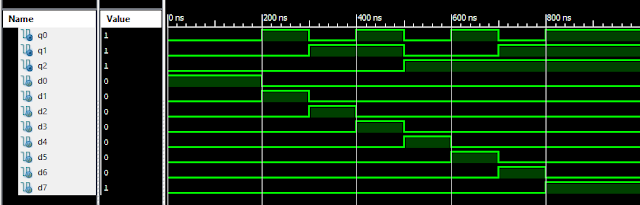
VLSI: 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling module encoder_8_to_3( input d0, input d1, input d2, input d3, input d4, input d5, input d6, input d7, output q0, output q1, output q2 ); assign q0 = ( d1 | d3 | d5 | d7 ); assign q1 = ( d2 | d3 | d6 | d7 ); assign q2 = ( d4 | d6 | d5 | d7 ); endmodule //Testbench code for 8-3 Encoder Dataflow Modelling initial begin ...
VLSI: 1-4 DEMUX (Demultiplexer) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_4( input d, input s0, input s1, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3 ); assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s0n = ~ s0; assign y0 = d& s0n & s1n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-4 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs ...
Verilog: 2 - 4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling with Testbench
Verilog Code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling 2-4 Line Decoder module decoder_2_to_4( input a0, input a1, output d0, output d1, output d2, output d3 ); not (an0,a0),(an1,a1); and (d0,an0,an1),(d1,a0,an1),(d2,an0,a1),(d3,a0,a1); endmodule //Testbench code for 2-4 Decoder Structural/Gate Level Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs a0 = 0;a1 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; a0=1;a1=0; #100; a0=0;a1=1; #100; a0=1;a1=1; end Output: Verilog 2-4 Decoder Response Other Verilog Programs: Go to Index of Verilog Prog...
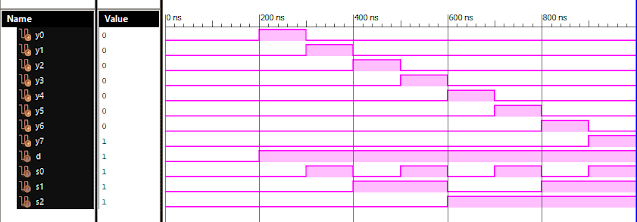
Verilog: 1to 8 DeMultiplexer (1-8 DEMUX) Dataflow Modelling with Testbench Code
Verilog Code for 1 to 8 DeMultiplexer Dataflow Modelling module demux_1_to_8( input d, input s0, input s1, input s2, output y0, output y1, output y2, output y3, output y4, output y5, output y6, output y7 ); assign s0n = ~ s0; assign s1n = ~ s1; assign s2n = ~ s2; assign y0 = d & s0n & s1n & s2n; assign y1 = d & s0 & s1n & s2n; assign y2 = d & s0n & s1 & s2n; assign y3 = d & s0 & s1 & s2n; assign y4 = d & s0n & s1n & s2; assign y5 = d & s0 & s1n & s2; assign y6 = d & s0n & s1 & s2; assign y7 = d & s0 & s1 & s2; endmodule //Testbench code for 1-8 DEMUX Dataflow Modelling initial begin // Initialize Inputs d = 0;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; // Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish #100; // Add stimulus here #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 0;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 1;s1 = 1;s2 = 0; #100; d = 1;s0 = 0;s1 = 0;s2 = 1; ...